ValidationTable of Contents
Table of Contents
API Platform Admin manages automatically two types of validation: client-side validation and server-side (or submission) validation.
# Client-side Validation
If the API documentation indicates that a field is mandatory, API Platform Admin will automatically add a required client-side validation.
For instance, with API Platform as backend, if you write the following:
<?php
// api/src/Entity/Book.php
namespace App\Entity;
use ApiPlatform\Metadata\ApiResource;
use Symfony\Component\Validator\Constraints as Assert;
#[ApiResource]
class Book
{
#[Assert\NotBlank]
public ?string $title = null;
}If you create a new book and try to submit without filling the “Title” field, you will see:

# Server-side Validation
When the form is submitted and if submission errors are received, API Platform Admin will automatically show the errors for the corresponding fields.
To do so, it uses the Server-Side Validation feature of React Admin, and the mapping between the response and the fields is done by the schema analyzer with its method getSubmissionErrors.
API Platform is supported by default, but if you use another backend, you will need to override the getSubmissionErrors method.
For example if you have this code:
<?php
// api/src/Entity/Book.php
namespace App\Entity;
use ApiPlatform\Metadata\ApiResource;
use Symfony\Component\Validator\Constraints as Assert;
#[ApiResource]
class Book
{
#[Assert\Isbn]
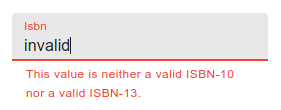
public ?string $isbn = null;
}If you submit the form with an invalid ISBN, you will see:
# Validation With React Admin Inputs
If you replace an <InputGuesser> with a React Admin input component, such as <TextInput>, <DateInput> or <ReferenceInput>, you will need to manually add the validation rules back.
Fortunately, this is very easy to do, thanks to the validate prop of the input components.
For instance, here is how to replace the input for the required title field:
import { EditGuesser, InputGuesser } from '@api-platform/admin';
import { TextInput, required } from 'react-admin';
export const BookEdit = () => (
<EditGuesser>
<InputGuesser source="title" />
<TextInput source="title" validate={required()} />
</EditGuesser>
);
React Admin already comes with several built-in validators, such as:
required(message)if the field is mandatory,minValue(min, message)to specify a minimum value for integers,maxValue(max, message)to specify a maximum value for integers,minLength(min, message)to specify a minimum length for strings,maxLength(max, message)to specify a maximum length for strings,number(message)to check that the input is a valid number,email(message)to check that the input is a valid email address,regex(pattern, message)to validate that the input matches a regular expression,choices(list, message)to validate that the input is within a given list
React Admin also supports Global Validation (at the form level).
Check out the Form Validation documentation to learn more.
You can also help us improve the documentation of this page.
