JWT Authentication
JSON Web Token (JWT) is a JSON-based open standard (RFC 7519) for creating access tokens that assert some number of claims. For example, a server could generate a token that has the claim “logged in as admin” and provide that to a client. The client could then use that token to prove that he/she is logged in as admin. The tokens are signed by the server’s key, so the server is able to verify that the token is legitimate. The tokens are designed to be compact, URL-safe and usable especially in web browser single sign-on (SSO) context.
API Platform allows to easily add a JWT-based authentication to your API using LexikJWTAuthenticationBundle.

Watch the LexikJWTAuthenticationBundle screencast
Installing LexikJWTAuthenticationBundle
We begin by installing the bundle:
$ docker-compose exec php composer require jwt-auth
Then we need to generate the public and private keys used for signing JWT tokens. If you’re using the API Platform distribution, you may run this from the project’s root directory:
$ docker-compose exec php sh -c '
set -e
apk add openssl
mkdir -p config/jwt
jwt_passphrase=${JWT_PASSPHRASE:-$(grep ''^JWT_PASSPHRASE='' .env | cut -f 2 -d ''='')}
echo "$jwt_passphrase" | openssl genpkey -out config/jwt/private.pem -pass stdin -aes256 -algorithm rsa -pkeyopt rsa_keygen_bits:4096
echo "$jwt_passphrase" | openssl pkey -in config/jwt/private.pem -passin stdin -out config/jwt/public.pem -pubout
setfacl -R -m u:www-data:rX -m u:"$(whoami)":rwX config/jwt
setfacl -dR -m u:www-data:rX -m u:"$(whoami)":rwX config/jwt
'
Note that the setfacl command relies on the acl package. This is installed by default when using the API Platform docker distribution but may need be installed in your working environment in order to execute the setfacl command.
This takes care of using the correct passphrase to encrypt the private key, and setting the correct permissions on the keys allowing the web server to read them.
Since these keys are created by the root user from a container, your host user will not be able to read them during the docker-compose build api process. Add the config/jwt/ folder to the api/.dockerignore file so that they are skipped from the result image.
If you want the keys to be auto generated in dev environment, see an example in the docker-entrypoint script of api-platform/demo.
The keys should not be checked in to the repository (i.e. it’s in api/.gitignore). However, note that a JWT token could
only pass signature validation against the same pair of keys it was signed with. This is especially relevant in a production
environment, where you don’t want to accidentally invalidate all your clients’ tokens at every deployment.
For more information, refer to the bundle’s documentation or read a general introduction to JWT here.
We’re not done yet! Let’s move on to configuring the Symfony SecurityBundle for JWT authentication.
Configuring the Symfony SecurityBundle
It is necessary to configure a user provider. You can either use the Doctrine entity user provider provided by Symfony (recommended), create a custom user provider or use API Platform’s FOSUserBundle integration (not recommended).
If you choose to use the Doctrine entity user provider, start by creating your User class.
Then update the security configuration:
# api/config/packages/security.yaml
security:
encoders:
App\Entity\User:
algorithm: argon2i
# https://symfony.com/doc/current/security.html#where-do-users-come-from-user-providers
providers:
# used to reload user from session & other features (e.g. switch_user)
app_user_provider:
entity:
class: App\Entity\User
property: email
firewalls:
dev:
pattern: ^/_(profiler|wdt)
security: false
main:
stateless: true
anonymous: true
provider: app_user_provider
json_login:
check_path: /authentication_token
username_path: email
password_path: password
success_handler: lexik_jwt_authentication.handler.authentication_success
failure_handler: lexik_jwt_authentication.handler.authentication_failure
guard:
authenticators:
- lexik_jwt_authentication.jwt_token_authenticator
access_control:
- { path: ^/docs, roles: IS_AUTHENTICATED_ANONYMOUSLY } # Allows accessing the Swagger UI
- { path: ^/authentication_token, roles: IS_AUTHENTICATED_ANONYMOUSLY }
- { path: ^/, roles: IS_AUTHENTICATED_FULLY }
You must also declare the route used for /authentication_token:
# api/config/routes.yaml
authentication_token:
path: /authentication_token
methods: ['POST']
If you want to avoid loading the User entity from database each time a JWT token needs to be authenticated, you may consider using
the database-less user provider provided by LexikJWTAuthenticationBundle. However, it means you will have to fetch the User entity from the database yourself as needed (probably through the Doctrine EntityManager).
Refer to the section on Security to learn how to control access to API resources and operations. You may also want to configure Swagger UI for JWT authentication.
Adding Authentication to an API Which Uses a Path Prefix
If your API uses a path prefix, the security configuration would look something like this instead:
# api/config/packages/security.yaml
security:
encoders:
App\Entity\User:
algorithm: argon2i
# https://symfony.com/doc/current/security.html#where-do-users-come-from-user-providers
providers:
# used to reload user from session & other features (e.g. switch_user)
app_user_provider:
entity:
class: App\Entity\User
property: email
firewalls:
dev:
pattern: ^/_(profiler|wdt)
security: false
api:
pattern: ^/api/
stateless: true
anonymous: true
provider: app_user_provider
guard:
authenticators:
- lexik_jwt_authentication.jwt_token_authenticator
main:
anonymous: true
json_login:
check_path: /authentication_token
username_path: email
password_path: password
success_handler: lexik_jwt_authentication.handler.authentication_success
failure_handler: lexik_jwt_authentication.handler.authentication_failure
access_control:
- { path: ^/api/docs, roles: IS_AUTHENTICATED_ANONYMOUSLY } # Allows accessing the Swagger UI
- { path: ^/authentication_token, roles: IS_AUTHENTICATED_ANONYMOUSLY }
- { path: ^/, roles: IS_AUTHENTICATED_FULLY }
Documenting the Authentication Mechanism with Swagger/Open API
Want to test the routes of your JWT-authentication-protected API?
Configuring API Platform
# api/config/packages/api_platform.yaml
api_platform:
swagger:
api_keys:
apiKey:
name: Authorization
type: header
The “Authorize” button will automatically appear in Swagger UI.
Adding a New API Key
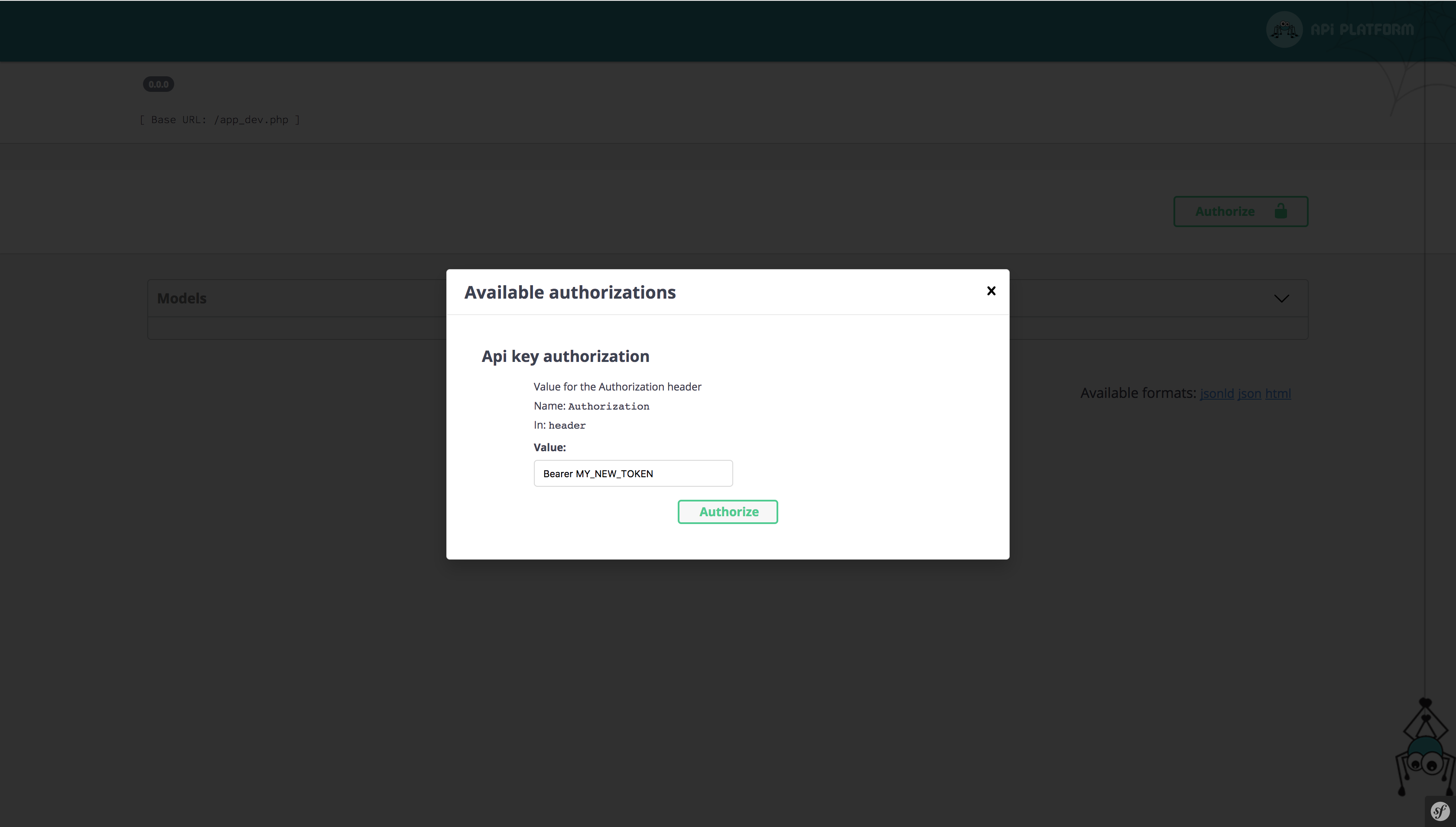
All you have to do is configure the API key in the value field.
By default, only the authorization header mode is enabled in LexikJWTAuthenticationBundle.
You must set the JWT token as below and click on the “Authorize” button.
Bearer MY_NEW_TOKEN
Adding endpoint to SwaggerUI to retrieve a JWT token
We can add a POST /authentication_token endpoint to SwaggerUI to conveniently retrieve the token when it’s needed.
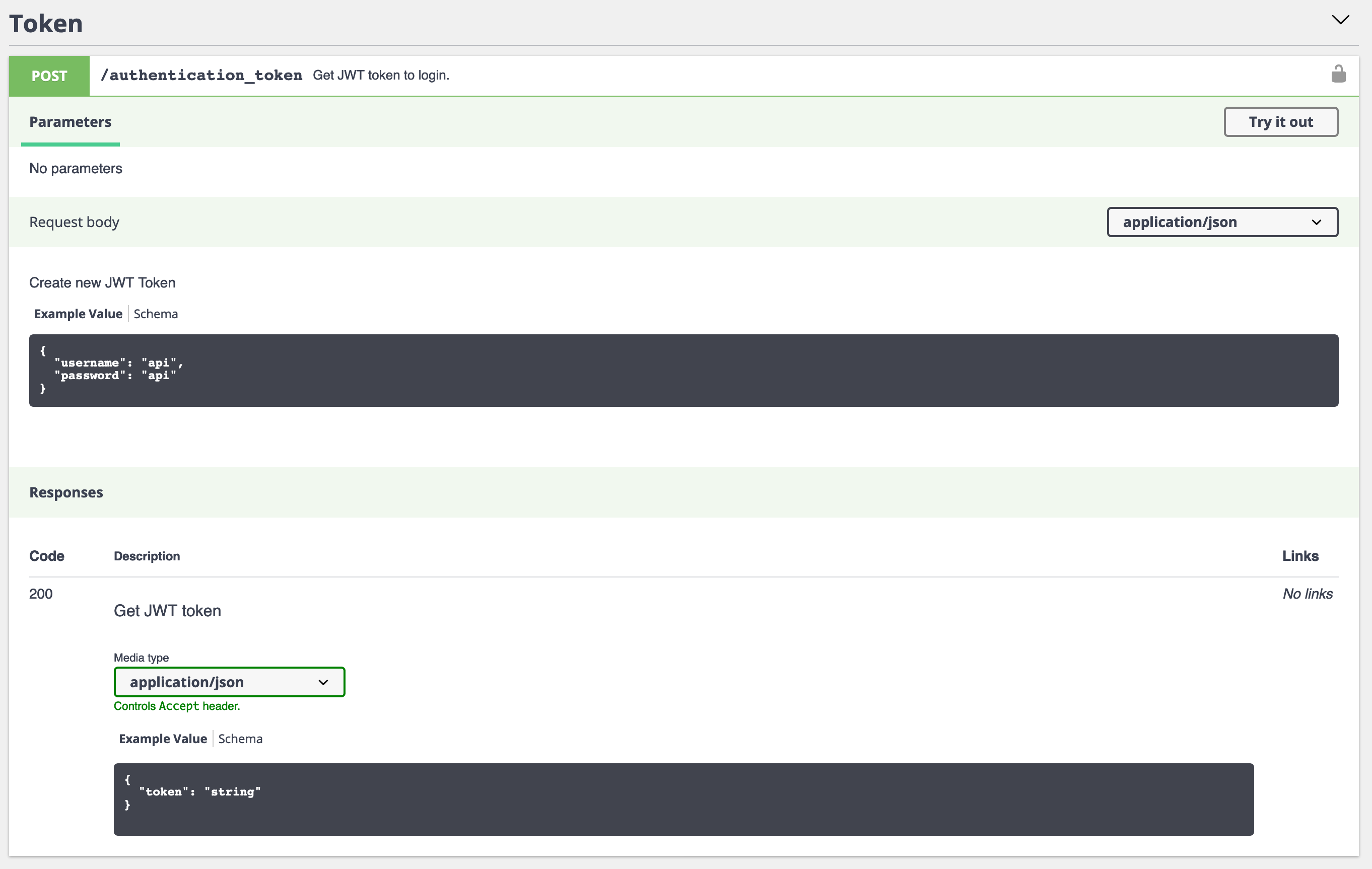
To do it, we need to create a SwaggerDecorator:
<?php
declare(strict_types=1);
namespace App\Swagger;
use Symfony\Component\HttpFoundation\Response;
use Symfony\Component\Serializer\Normalizer\NormalizerInterface;
final class SwaggerDecorator implements NormalizerInterface
{
private NormalizerInterface $decorated;
public function __construct(NormalizerInterface $decorated)
{
$this->decorated = $decorated;
}
public function supportsNormalization($data, string $format = null): bool
{
return $this->decorated->supportsNormalization($data, $format);
}
public function normalize($object, string $format = null, array $context = [])
{
$docs = $this->decorated->normalize($object, $format, $context);
$docs['components']['schemas']['Token'] = [
'type' => 'object',
'properties' => [
'token' => [
'type' => 'string',
'readOnly' => true,
],
],
];
$docs['components']['schemas']['Credentials'] = [
'type' => 'object',
'properties' => [
'username' => [
'type' => 'string',
'example' => 'api',
],
'password' => [
'type' => 'string',
'example' => 'api',
],
],
];
$tokenDocumentation = [
'paths' => [
'/authentication_token' => [
'post' => [
'tags' => ['Token'],
'operationId' => 'postCredentialsItem',
'summary' => 'Get JWT token to login.',
'requestBody' => [
'description' => 'Create new JWT Token',
'content' => [
'application/json' => [
'schema' => [
'$ref' => '#/components/schemas/Credentials',
],
],
],
],
'responses' => [
Response::HTTP_OK => [
'description' => 'Get JWT token',
'content' => [
'application/json' => [
'schema' => [
'$ref' => '#/components/schemas/Token',
],
],
],
],
],
],
],
],
];
return array_merge_recursive($docs, $tokenDocumentation);
}
}
And register this service in config/services.yaml:
services:
# ...
App\Swagger\SwaggerDecorator:
decorates: 'api_platform.swagger.normalizer.documentation'
arguments: ['@App\Swagger\SwaggerDecorator.inner']
autoconfigure: false
Testing
To test your authentication with ApiTestCase, you can write a method as below:
<?php
// tests/AuthenticationTest.php
namespace App\Tests;
use ApiPlatform\Core\Bridge\Symfony\Bundle\Test\ApiTestCase;
use App\Entity\User;
use Hautelook\AliceBundle\PhpUnit\ReloadDatabaseTrait;
class AuthenticationTest extends ApiTestCase
{
use ReloadDatabaseTrait;
public function testLogin(): void
{
$client = self::createClient();
$user = new User();
$user->setEmail('[email protected]');
$user->setPassword(
self::$container->get('security.password_encoder')->encodePassword($user, '$3CR3T')
);
$manager = self::$container->get('doctrine')->getManager();
$manager->persist($user);
$manager->flush();
// retrieve a token
$response = $client->request('POST', '/authentication_token', [
'headers' => ['Content-Type' => 'application/json'],
'json' => [
'email' => '[email protected]',
'password' => '$3CR3T',
],
]);
$json = $response->toArray();
$this->assertResponseIsSuccessful();
$this->assertArrayHasKey('token', $json);
// test not authorized
$client->request('GET', '/greetings');
$this->assertResponseStatusCodeSame(401);
// test authorized
$client->request('GET', '/greetings', ['auth_bearer' => $json['token']]);
$this->assertResponseIsSuccessful();
}
}
Refer to Testing the API for more information about testing API Platform.
You can also help us improve the documentation of this page.
